In this unit you will ...
- explore the function and structure of the nervous system.
- investigate the interaction of the nervous system with other systems (locomotor system,...).
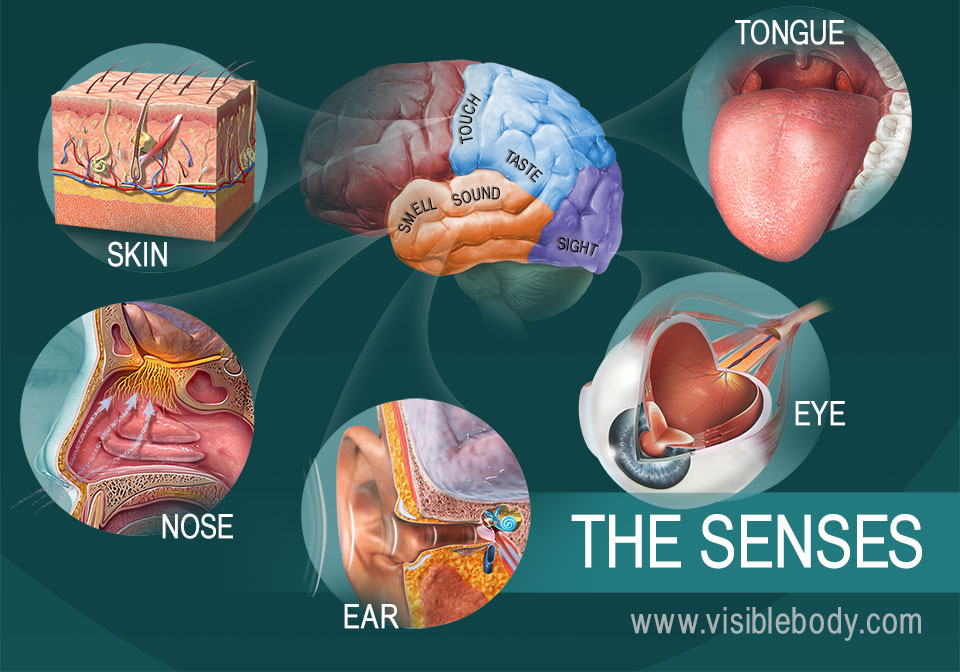
We perceive the world through our senses. Sight, touch, smell, hearing and taste aloow us to explore the environment around us. All the information received by our senses is processed by our most important organ, the brain. The brain is home to the conscious and unconscious mind, as well as our emotions and memory. It controls our involuntary actions, such us breathing or digesting food, as well as our thinking and decision making. What other types of involuntary actions do we have?

1. The nervous system

SENSORY NEURONS: Collect information from our sense organs (skin, eyes, nose, tongue).
MOTOR NEURONS: Send messages from the brain to our locomotor system.
Activity 1: Fill in the blanks.
the cells in our body that carry the electrical signals through out our bodies.
.
the
body’s
main
information
center
,
where
information
is
received
and
processed
.
neurons
that
are
attached
to
the
spine
, information
.
Brain
Brain-
Brain-
Spinal
Neurons-
cord-
1.1. What is the Nervous System?
The nervous system is the control center of the body.It is responsible for control and communication of your body.
The nervous system sends messages from the brain to different parts of the body, such us to respond to the stimuli from our senses. It also controls our internal systems such as the digestive or respiratory systems.
The nervous system is the control center of the body.It is responsible for control and communication of your body.
The nervous system sends messages from the brain to different parts of the body, such us to respond to the stimuli from our senses. It also controls our internal systems such as the digestive or respiratory systems.
1.2.CENTRAL AND PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
It’s
divided into two main systems, the central
nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
A. The central
nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal
cord (médula espinal).
a.1. In the brain we can distinguish three parts:
1.The cerebrum (cerebro)
2.The
cerebellum (cerebelo)
3.The
brain stem (bulbo raquídeo)
a.2. The spinal cord is located in the back. It controls involuntary movements. It runs down a tunnel of holes in our backbone. The bones, called vertebrae, protect it from damage.
B. The Peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves. The brain communicates with the rest of the body through the spinal cord and the nerves.
Nerves carry information from the organs to the brain and from the brain to the rest of the body. Nerves are made up of tiny cells called neurons or nerve cells, they receive and transmit information.





1.3.
REFLEX AND VOLUNTARY MOVEMENTS
We can distinguish two types of movements:
a. Reflex movements (movimientos reflejo): they are involuntary movements in response to external stimuli.
b. Voluntary movements: They are the result of decisions.
Nerves carry information from the organs to the brain and from the brain to the rest of the body. Nerves are made up of tiny cells called neurons or nerve cells, they receive and transmit information.
*THE CEREBRUM
We can distinguish two types of movements:
a. Reflex movements (movimientos reflejo): they are involuntary movements in response to external stimuli.
b. Voluntary movements: They are the result of decisions.
Extra material:
https://youtu.be/bz7hj_YC3j0
3D MODEL NERVOUS SYSTEM: https://www.zygote.com/poly-models/3d-male-systems/3d-male-nervous-system
Let´s review!
1. What protects our brain?
2. Name the parts of the central nervous system.
3. Explain the role of the cerebellum when you learn how to ride a bike.
4. Decide if the following movements are voluntary (V) or involuntary (I).
a. breathing
b.playing the guitar
c.blinking
d. jumping over a wall
e. blood circulation
5. Why do eyes have eyelashes and eyelids?
6. We use our ears to hear. What other function do our ears have?
7. How are our senses of smell and taste connected? What can happen if we have a cold?
8. What do sensors in our skin detect?
9. What healthy habits can protect our sense organs?
10. Complete the sentences in your notebook.
a. The ..... is a muscle that makes the pupil bigger or smaller.
b. In the ......vibrations are transformed into electrical signals.
c. The receptor cells for taste are on the ...... inside each taste bud.
11. What is the difference between ligaments and tendons?
12. What is the musculoskeletal system made up of?
13. Classify the following bones as long (L), short (S) or flat (F).
femur - scapula - clavicle - vertebrae - humerus - ribs
14. What are the functions of the skeleton?
15.. Which bones protect the respiratory system?
16. Label the parts of the brain using the words in the box. There are some extra words.








Nice article provides useful information and spreads the knowledge about the healthy life must read
ResponderEliminarCPR in Highland