1. Healthy Eating Habits
A. INTRODUCTION
A healthy diet is a balanced diet. We need to eat the right amounts of the different food groups. Each food group helps our body in different way. If we do not follow a balanced diet, we feel tired, we can´t concentrate, we don´t feel well and we can have health problems.
As you know, we obtein nutrients from food. Nutrients are the substances which plants and animals need in order to live and grow. The digestive system is the group of organs in the body that extract nutrients from food and expel undigested waste.
B. FOOD GROUPS
1. Bread and cereals.
2. Fruit and vegetables.
3. Meat, fish, egg and beans.
4. Milk and dairy.
5. Good vegetables oils and fats.
C. FOOD PYRAMID
A food pyramid or diet pyramid is a triangular diagram representing the optimal number of servings to be eaten each day from each of the basic FOOD GROUPS.
It is illustrative and depends on where you live. Our ideal food pyramid is the mediterranean food pyramid.
C. SUGGESTED SERVINGS/PORTIONS FROM EACH FOOD GROUP (*in my opinion):
- Cereal and Grains Group: You should eat at least six servings a day.
- Fruit and Vegetable Group: You should eat at least five or six servings a day.
- Meat, Fish and Eggs Group: You should eat about two servings a day.
- Good Fats Group: You should eat in small amounts (30g approx. a day).
- Milk and Dairy Group: You should eat about two servings a day.
- Sugary Food and Bad Fats Group: You should not eat (only on party or school birthdays).
.
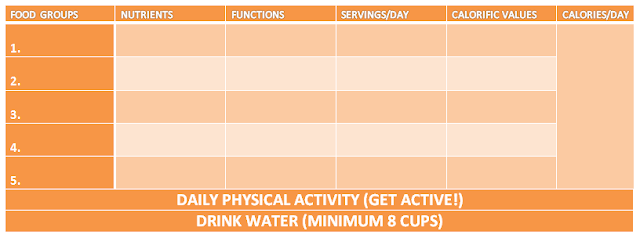
D. FOOD GROUPS, NUTRIENTS AND FUNCTIONS
E. HOW MANY CALORIES DO WE NEED A DAY TO BE HEALTHY?
Our bodies need energy to work. A calorie is a unit of energy.
In nutrition, calories refer to the energy people get from the food and drink they consume, and the energy they use in physical activity.
Calories are listed in the nutritional information on all food packaging.
a. Daily requirement
Not everybody needs the same number of calories each day. People have different metabolisms that burn energy at different rates, and some people have more active lifestyles than others.
The recommended intake of calories per day depends on several factors, including:
- general health
- physical activity demands
- sex
- weight
- height
So, you should intake about 2.000 kcal / 2700 Kcal per day.
b. Calories and health
The human body needs calories to survive. Without energy, the cells in the body would die, the heart and lungs would stop, and the organs would not be able to carry out the basic processes needed for living. People absorb this energy from food and drink.
If people consumed only the number of calories needed every day, they would probably have healthy lives. Calorie consumption that is too low or too high will eventually lead to health problems.
The number of calories in food tells us how much potential energy they contain. It is not only calories that are important, but also the substance from which the calories are taken.
Below are the calorific values of three main components of food:
- 1 g of carbohydrates contains 4 kcal
- 1 g of protein contains 4 kcal
- 1 g of fat contains 9 kcal
c. Empty calories
Empty calories are those that provide energy but very little nutritional value.
Sources of empty calories.
The following foods and drinks provide the largest amounts of empty calories:
Solid fats and added sugars: ice cream, cookies, cakes,...
Solid fats: ribs, bacon, hot dogs, sausages, pizza, ...
Added sugars: fruit drinks, sports drinks, energy drinks,...
SUMMARY TIME!
Complete the following summary table:
F. PIRÁMIDE NAOS Y CALENDARIO ACTIVIDAD FÍSICA.
a. Pirámide Naos.
b. Calendario actividad física.